Solutions for Robotics

Enhancing Vision-Based Robots with IMUs from MicroStrain
In the ever-evolving landscape of robotics, particularly in autonomous systems, the integration of various sensory technologies is not just a trend, but a necessity. While vision systems, like cameras and LiDAR, are pivotal in navigation and environmental interaction, there’s an emerging consensus on the benefits of incorporating an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) into these robots. This article delves into the practical scenarios where adding an IMU to a vision-system-equipped autonomous robot is not just beneficial, but essential.
Detail

MICROSTRAIN INERTIAL SENSORS GUIDE UNMANNED GROUND VEHICLES
MicroStrain’s miniature, lightweight inertial navigation solutions improve navigational accuracy while reducing power consumption in next-generation unmanned ground vehicles (UGV).
Detail

GQ7 VS GX5 PRODUCT COMPARISON TEST REPORT
The new 3DMGQ7-GNSS/INS builds on the success of the 3DMGX5-GNSS/INS and adds many features desired by customers which resolve common challenges in specific use cases. This test report highlights four evolutionary improvements.
- Test 1: Dual-Antenna Stationary Heading
- Test 2: Magnetic Interference Immunity
- Test 3: Dual-Antenna + RTK vs Single-Antenna
- Test 4: Wheel Odometry Aiding during GNSS Attenuation

Product Comparison: GX5 Series vs. GV7 Series
The GV7 series of inertial sensors offers improved performance and functionality over the GX5 series while maintaining the same compact size and easy-to-replace design. This upgrade is ideal for those seeking higher accuracy and additional features.

Enhancing Inertial Navigation System Performance with Radar
By leveraging the strengths of both radar and INS, engineers and researchers can develop more capable and adaptable autonomous robots for a variety of applications, from industrial automation to autonomous vehicles.

Analysis of MIP vs NMEA Aiding Information with the MicroStrain 3DM-CV7-INS
MicroStrain Field Applications Engineer, Aidan Laracy, did a deep dive to compare the performance of NMEA and MIP GNSS data input methods for the 3DM-CV7-INS. Learn as he explores the trade-offs between ease of integration and precision.

Pushing the Boundaries of Humanoid Robot Performance with Westwood Robotics
Developing humanoid robots involves an intricate blend of disciplines, including mechanical engineering, electronics, computer science, and artificial intelligence. THEMIS stands as a testament to these complex challenges.
MicroStrain’s 3DM-CV7-AHRS (attitude and heading reference system) inertial sensor was integrated into THEMIS to provide information about the robot’s orientation (roll, pitch, and yaw) and its acceleration.
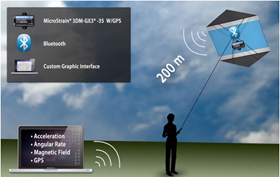
LIGHTWEIGHT INERTIAL SENSOR MONITORS REAL-TIME ORIENTATION AND GPS DURING FLIGHT
Miniature Attitute Heading Reference System with build in GPS wirelessly communicate continuous acceleration, angular rate, magnetic field, and location data without impacting flight performance.
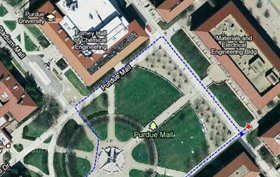
PRECISE VIRTUAL PEDOMETRY USING MINIATURE INERTIAL SENSORS
Cost effective inertial sensors demonstrate accurate dead-reckoning positioning in two and three dimensions for more precise and reliable personnel tracking.
Detail

SETTING SAIL ON THE PACIFIC SPIRIT
A case study of the Microstrain 3DM-GQ7 with dual antenna and RTK modem to collect navigation and position data using SensorConnect Software.
Detail

Vibrating Robots – Case Study
A Prosig system is used to capture CAN bus data and vibration signals on an industrial robot. Control is by CAN bus and the Prosig P8000 compares sending commands to the robot and seeing the vibration effects caused by the displacement of the hydraulics.
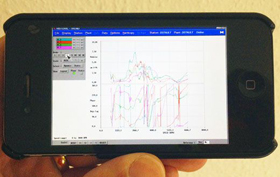
Remote Monitoring – Case Study
Have you ever wondered if there is a vibration condition monitoring system that can be installed anywhere and then monitored from anywhere else? Even on your smartphone?
Detail
Research Facilities
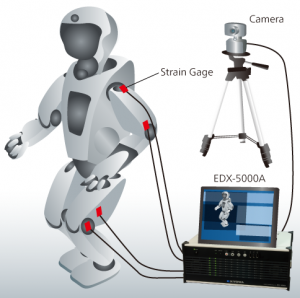
Stress measurement of the movable parts of robots
Memory Recorder/Analyzer EDX-5000A enables multichannel measurements, such as the stress measurement of the movable parts of a robot and the simultaneous recording of videos.